Ma Plots Explanation
- Summaries A lonely woman befriends a group of teenagers and decides to let them party at her house. Just when the kids think their luck couldn't get any better, things start happening that make them question the intention of their host.
- Scatterplots are useful for interpreting trends in statistical data. Each observation (or point) in a scatterplot has two coordinates; the first corresponds to the first piece of data in the pair (that’s the X coordinate; the amount that you go left or right). The second coordinate corresponds to the second piece of data in the.
- Third and fourth graders learn about basic reading concepts including the various parts of plot, as well as characters and setting. Parents and students can work together at home to reinforce what a child learns in school. Read on to learn more about identifying characters, determining the setting, and understanding the plot of a book or story.
| plotMA {limma} | R Documentation |
MA-Plot of Expression Data

Ma (2019) Plot Summary (4) A lonely woman befriends a group of teenagers and decides to let them party at her house. Just when the kids think their luck couldn't get any better, things start happening that make them question the intention of their host. 'the MA plot is supposed to detect some artifacts' I agree with Ryan. It's maybe counterproductive to consider the MA plot.only. as a tool for diagnosing problems. And I wouldn't go down the path of trying to force the center of the LFCs to the y=0 line. That's definitely too heavy handed in my opinion for RNA-seq data.
Description
Creates an MA-plot with color coding for control spots.
Usage
Arguments
object | an |
array | integer giving the array to be plotted. |
coef | integer giving the linear model coefficient to be plotted. |
xlab | character string, label for x-axis |
ylab | character string, label for y-axis |
main | character string, title for plot |
status | vector giving the control status of each spot on the array, of same length as the number of rows of |
zero.weights | logical, should spots with zero or negative weights be plotted? |
... | other arguments are passed to |
Ma Plots Explanation
Details
An MA-plot is a plot of log-intensity ratios (M-values) versus log-intensity averages (A-values).See Ritchie et al (2015) for a brief historical review.
For two color data objects, a within-array MA-plot is produced with the M and A values computed from the two channels for the specified array.This is the same as a mean-difference plot (mdplot) with the red and green log2-intensities of the array providing the two columns.
For single channel data objects, a between-array MA-plot is produced.An artificial array is produced by averaging all the arrays other than the array specified.A mean-difference plot is then producing from the specified array and the artificial array.Note that this procedure reduces to an ordinary mean-difference plot when there are just two arrays total.
If object is an MArrayLM object, then the plot is an fitted model MA-plot in which the estimated coefficient is on the y-axis and the average A-value is on the x-axis.
The status vector can correspond to any grouping of the probes that is of interest.If object is a fitted model object, then status vector is often used to indicate statistically significance, so that differentially expressed points are highlighted.If object is a microarray data object, then status might distinguish control probes from regular probes so that different types of controls are highlighted.
The status can be included as the component object$genes$Status instead of being passed as an argument to plotMA.
See plotWithHighlights for how to set colors and graphics parameters for the highlighted and non-highlighted points.
Value
A plot is created on the current graphics device.
Note
The plotMD function provides the same functionality as plotMA with slightly different arguments.
Author(s)
Gordon Smyth
References
Ritchie, ME, Phipson, B, Wu, D, Hu, Y, Law, CW, Shi, W, and Smyth, GK (2015).limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies.Nucleic Acids Research Volume 43, e47.http://nar.oxfordjournals.org/content/43/7/e47
See Also
The driver function for plotMA is plotWithHighlights.
An overview of plot functions available in LIMMA is given in 09.Diagnostics.
Examples
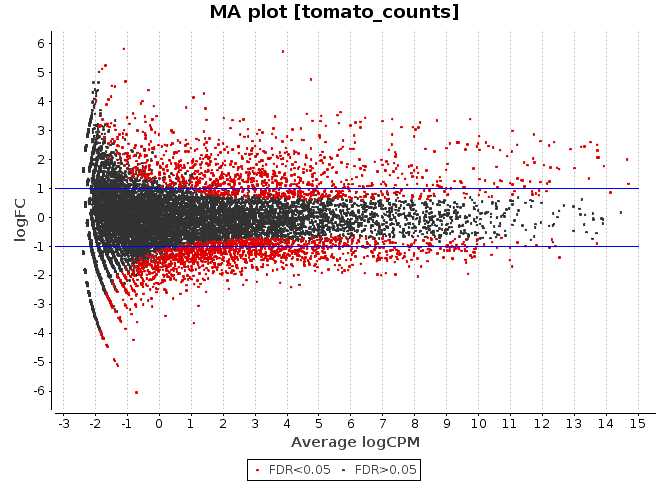
I have a RNA-seq dataset of tumor and control samples. I plotted two MA plots, before and after normalization (plotSmear with Bioconductor). I don't understand how to know it the results are ok just by looking at the shape. My professor explained that if the 'dot cloud' has a trumpet shape, it is good. But then in some exercise examples he shows MA plots with different shapes that are also ok.I would appreciate an explanation for 'dummies' on this as I am a newbie. I forgot to say that I have already read the wikipedia page about MA plots and some articles about RNA-seq with no luck. Thanks in advance.
It would be better to give an image of the plots in question.
If you can't provide that then please tell us what are your X and Y axis labels?
Ma Plots Explanation Template
Sorry for my late reply. The X label is logCPM and the Y label logFC (tumor-control).